Data Engineering Digest, October 2025
Hello Data Engineers,
Welcome back to another edition of the data engineering digest - a monthly newsletter containing updates, inspiration, and insights from the community.
Here are a few things that happened this month in the community:
The best GUI-based ETL tools in 2025.
Semantic layers: hyped or actually valuable?
Partitioning vs clustering best practices.
dbtran: the dbt + Fivetran merger.
How Uber standardizes mobile analytics.
Rebuilding Uber’s query architecture.
Community Discussions
Here are the top posts you may have missed:
1. Best GUI-based Cloud ETL/ELT
One community member shared how their team transitioned from Informatica PowerCenter to a modern Databricks stack using Scala and PySpark. While the shift brought flexibility, developing complex gold-layer models became slower and harder to debug. They plan to keep Databricks for their bronze and silver layers but reintroduce a GUI-based tool for the gold layer to simplify deployment hence the question.
The community generally favors code-first tools for flexibility and to avoid vendor lock-in - though newer no-code platforms have evolved significantly since the early days of data engineering. For example, some newer tools allow you to switch between code/GUI and allow you to export the underlying code to avoid lock-in.
💡 Key Insight
Coalesce.io was a popular suggestion for its integration with Databricks and flexible GUI features. Some users did mention that migrating SQL to Coalesce was a pain point. Matillion was also mentioned a few times as a solid tool but with high vendor lock-in. A few also mentioned that dbt cloud has a nice GUI feature called dbt canvas.
2. What’s the community’s take on semantic layers?
Semantic layers are experiencing a renaissance as organizations look to make their data more accessible to both humans and now AI systems. We talked about this in our AI agents trend discussion back in June.
The semantic layer is a translation layer between your raw data and the people or tools using it. In other words, it defines what your data means - things like how to calculate “revenue,” what counts as an “active user,” or how different tables relate to each other.
💡 Key Insight
Semantic layers have existed for decades, traditionally tied to BI tools. Now, standalone platforms are gaining traction - especially because AI systems need shared definitions and context to produce reliable results. Modern tools let you decouple the semantic layer from both your BI tool and database, giving teams far more flexibility and control. Overall, these modern semantic layers are being heavily invested in by both companies and data engineers alike.
3. Is Partitioning data in Data Lake still the best practice?
Snowflake and Databricks don’t do partitioning anymore. Both use clustering to co-locate data and they seem to be performant enough…But what does Snowflake or Databricks do differently that avoids partitioning entirely?
💡 Key Insight
In data lakes where data is stored as files, partitioning refers to how you organize the files in “folders” (like year=2025/month=03/myfile.parquet). Partitioning often happens on common filtering fields like date to help a query engine quickly find or update data by that field.
Clustering on the other hand uses metadata about the files to order the data inside the data lake. This also helps query engines skip over irrelevant data. In some systems this clustering is “virtual” meaning the files don’t move but in others the data is physically co-located together based on the clustering keys.
TL;DR Partitioning remains a simple, transparent way to prune large datasets and it still pairs well with clustering for optimal performance. You might for example start with a coarse partition (e.g., by date) and add clustering within partitions on other changing dimensions like customer_id, region, or product_category.
Industry Pulse
Here are some industry topics and trends from this month:
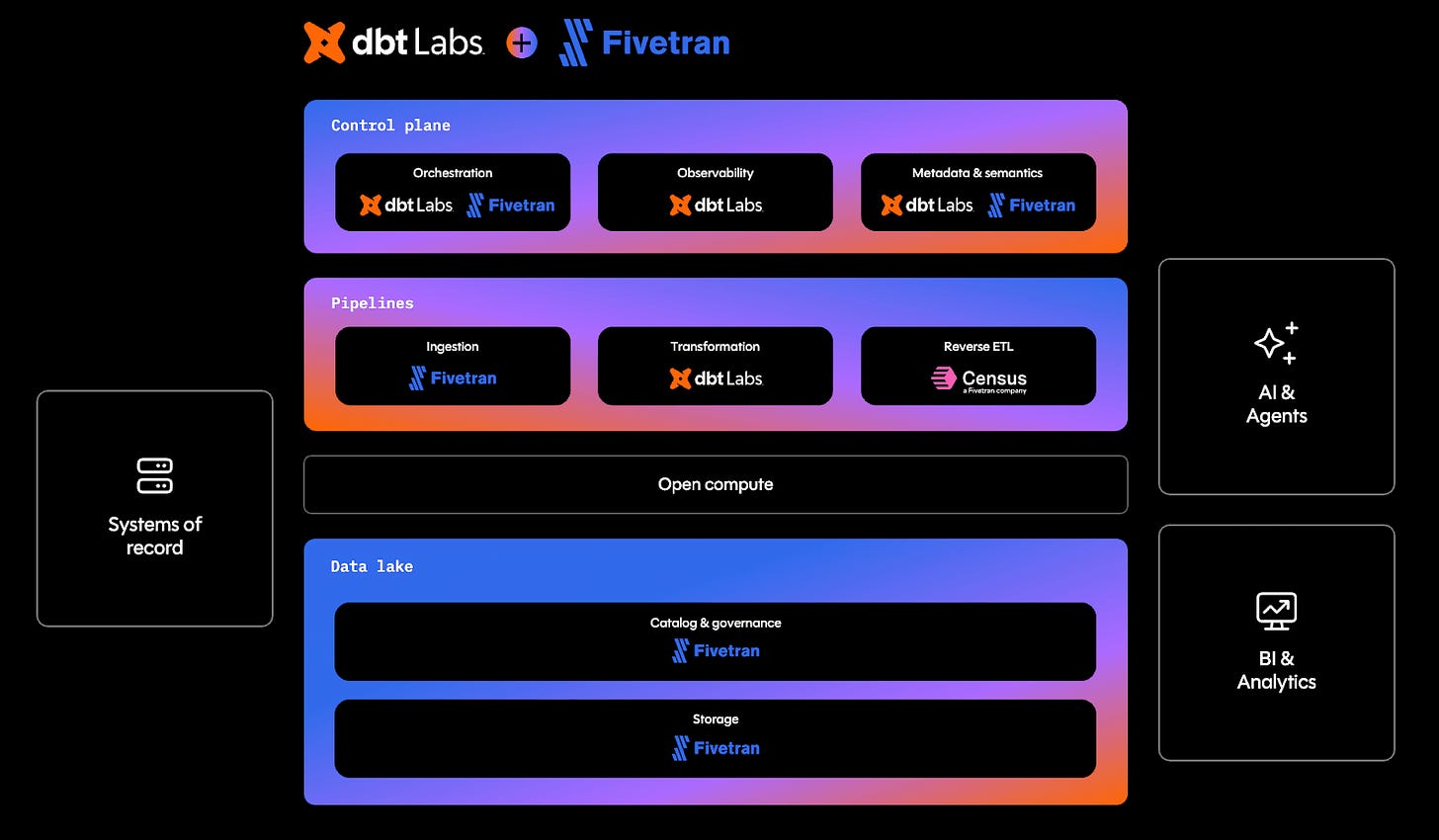
1. dbtran: dbt + Fivetran’s merger
This month, the rumors were revealed to be true when Fivetran and dbt Labs announced a merger between the two companies creating a combined data infrastructure company with nearly $600 million in annual revenue.
The community also shared perspectives on why this deal makes sense and introduced a new open-source fork of dbt, OpenDBT.
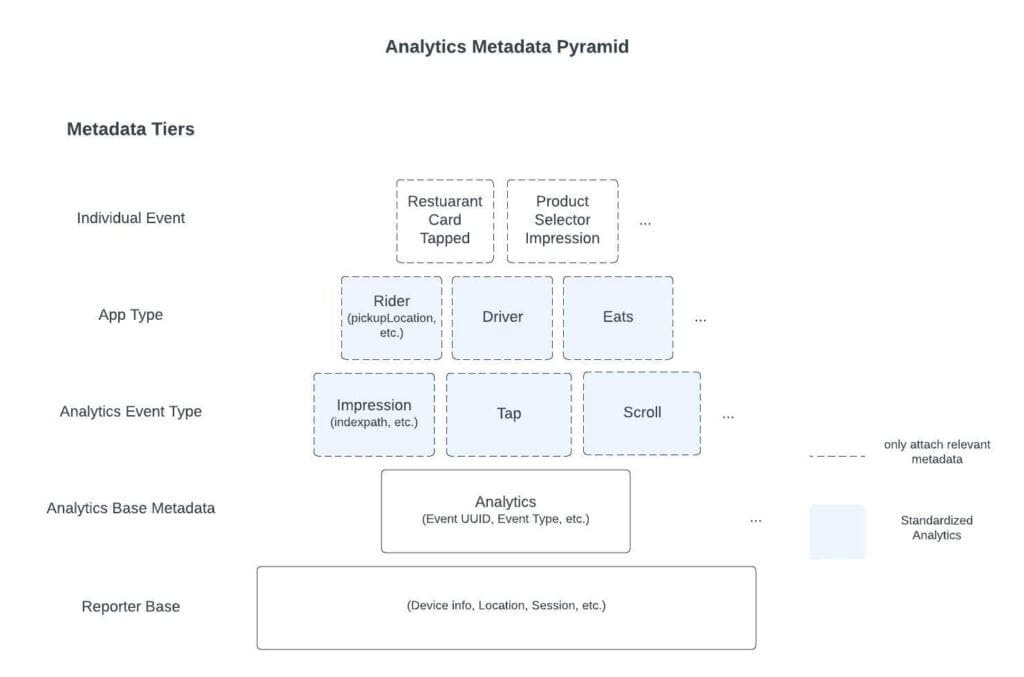
2. How Uber Standardized Mobile Analytics for Cross-Platform Insights
Uber rebuilt its mobile tracking system so all its apps collect data the same way. Before, each team tracked taps and views differently, which made the data messy and hard to trust. Now, shared tools automatically record common actions and details, saving engineers time and improving accuracy.
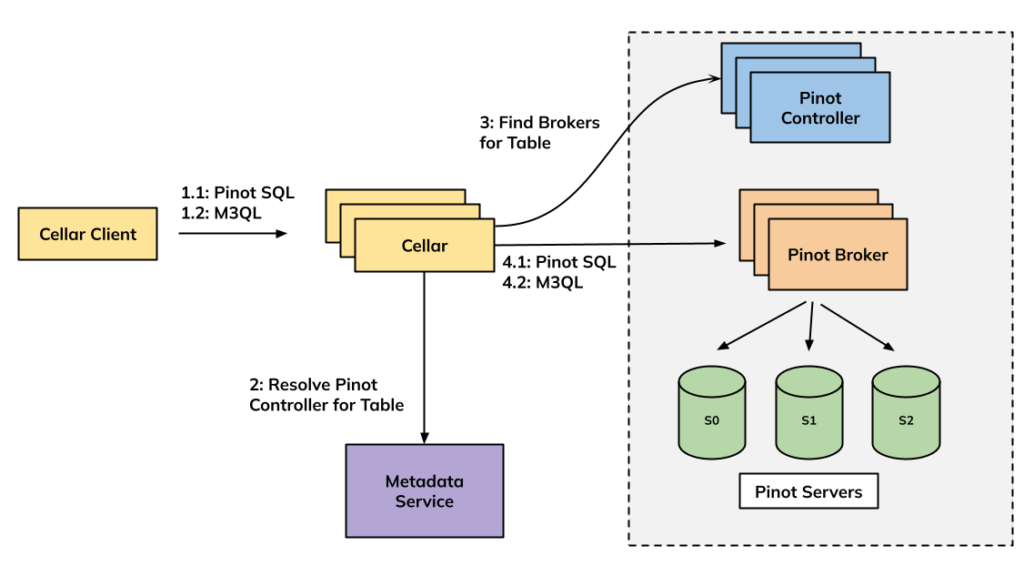
3. Rebuilding Uber’s Apache Pinot™ Query Architecture
In another post from Uber engineering they rebuilt their real-time analytics system to move away from their older query engine, called Neutrino, which added extra layers and made queries harder to manage. The new setup uses Apache Pinot’s built-in engines, including a lighter “Lite Mode” that keeps queries fast and safe by setting smart limits. A new tool called Cellar now connects users directly to Pinot, making it simpler, faster, and more reliable for both regular and complex data searches. This change gives Uber better performance, clearer control, and a cleaner path toward retiring Neutrino in the future.
🎁 Bonus:
📅 Upcoming Events
No events - check back next month!
Share an event with the community here or view the full calendar
Opportunities to get involved:
What did you think of today’s newsletter?
Your feedback helps us deliver the best newsletter possible.
If you are reading this and are not subscribed, subscribe here.
Want more Data Engineering? Join our community.
Stay tuned next month for more updates, and thanks for being a part of the Data Engineering community.